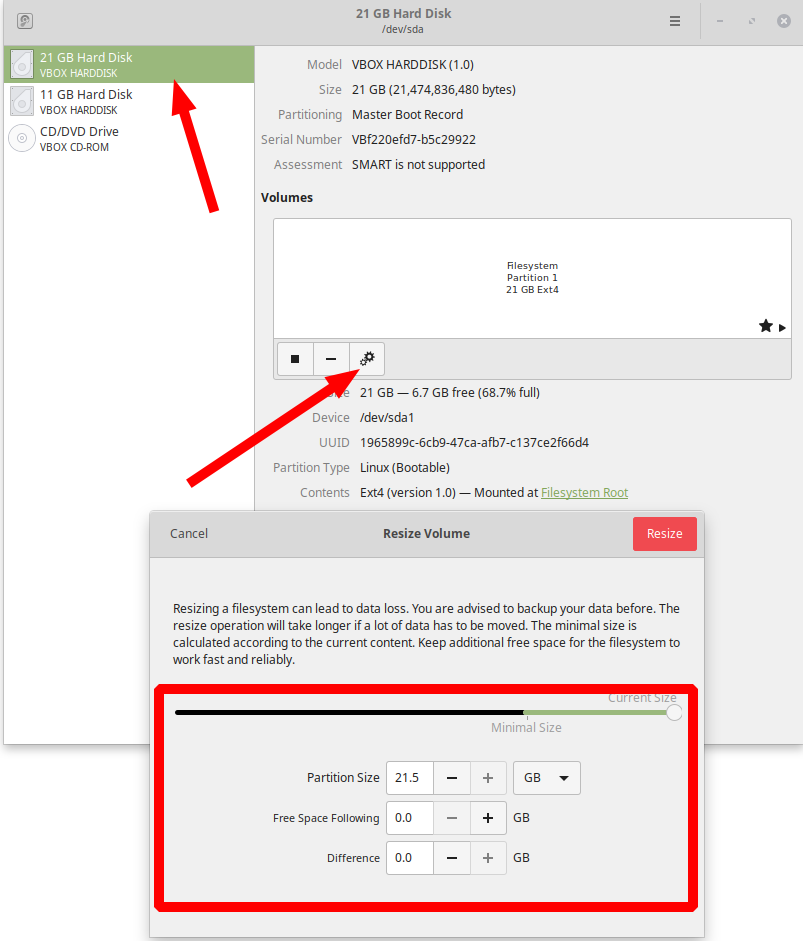
Unique Tips About How To Increase Stack Size Linux

You can query the maximum process and stack sizes using getrlimit.
How to increase stack size linux. I have created a ramdisk of 8 mb using the following commands: It depends on how much local data (i.e., local variables). If even setting stack within.
Typically the logic would be: The stack size, refers to how much space in memory is allocated for the stack. Increasing the stack size on windows, linux, and unix systems.
First of all, it is 8192 kilo bytes, and not bytes. 0 you can try writing a script (where you set the ulimit) in /etc/init.d/ directory. I know that stacks are limited to.
2 answers sorted by: Call getrlimit to get current. Normally you would set the stack size early on, e,g, at the start of main(), before calling any other functions.
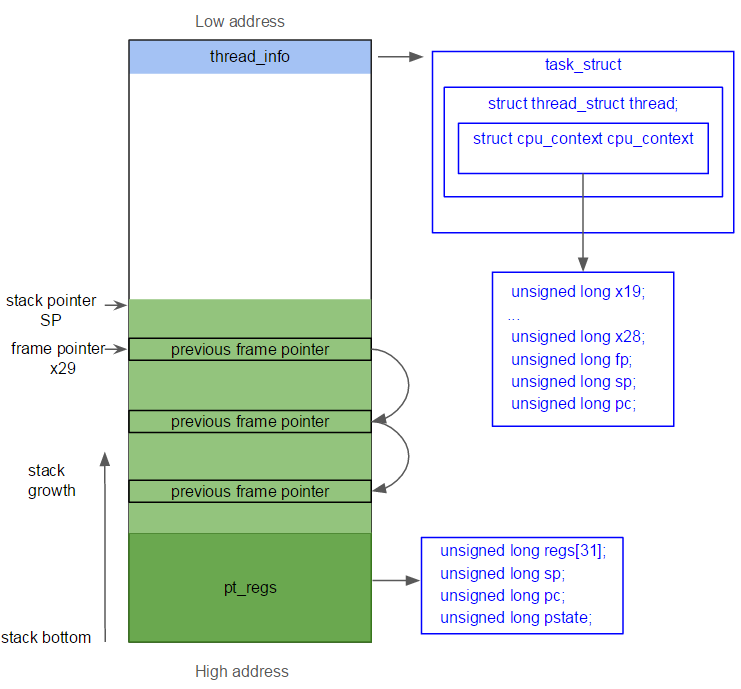
Overview the kernel stack and the user stack are implemented using the stack data structure and, taken together, serve as a call stack. I'm looking for a good description of stacks within the linux kernel, but i'm finding it surprisingly difficult to find anything useful. Furthermore stack is one thing, variable is another, and heap yet another.
See linux process stack overrun by local variables (stack guarding) for more about compiler options for hardening against that, e.g. Knowledgebase increasing the stack size in shell is resulting in an increase in virtual memory size for multithrea. By default the linux network stack is not configured for high speed large file transfer across wan links.
If current size < required stack size then call setrlimit to increase stack size. The memory will be paged in as required. Stack frames don't have a fixed size;
If the stack size is too small, you can increase it by changing operating system settings, changing compiler settings, or using the alloca function. Via stack probes to make. Increase the stack size on windows, linux, and unix systems by setting the.
Increasing the stack size in shell is resulting in an. Increasing the stack size allows the program to increase the number of routines This is done to save memory resources.
Viewed 1k times. Using /etc/security/limits.conf will set them permanently but you have to relogin ( new session ) to they can be effective. Typically the logic would be:






![[BUG] Increase in stack size ConanExiles](https://external-preview.redd.it/elipdXf75kUGIQVeGz0-tmDHiXJ3J4mr6XNwe71V6NY.jpg?auto=webp&s=77db626ba290e46f861e2835f38d4d1cd67934cf)


![[java] Java stack overflow error how to increase the stack size in](https://i.stack.imgur.com/xyzQC.png)


